Turnover statistics
Average time to find at least 2 reviewers after submission = 26 days (median = 17)
Average time from submission to 1st decision = 68 days (median = 57)
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▲ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
20 Sep 2023
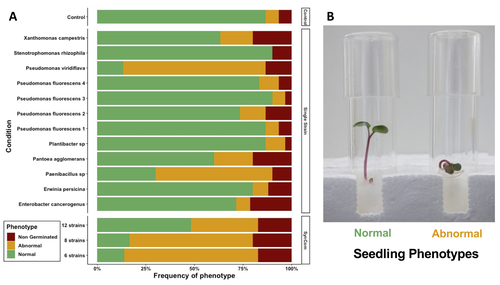
Transmission of synthetic seed bacterial communities to radish seedlings: impact on microbiota assembly and plant phenotypeMarie Simonin, Anne Preveaux, Coralie Marais, Tiffany Garin, Gontran Arnault, Alain Sarniguet, Matthieu Barret https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.14.527860Seed synthetic community matters and its impact on seedling is strain- and not species-dependantRecommended by Sebastien Massart based on reviews by Cindy Morris, Sebastian Pfeilmeier and 1 anonymous reviewerEngineering plant microbiota can improve plant health and growth sustainably. Emergent approaches include rational Synthetic Communities (SynCom) design or soil amendments and specific agricultural practices to shift resident microbiota and to understand its impact (Moreira et al. 2023). In this context, the impact of seed microbiota on the early stages of plant development is becoming an essential topic in the study of plant–microbiota interactions. Behind the well-studied seed-borne pathogens, the seed microbiota can host many other commensal and beneficial organisms that have been neglected in the past. The study of Simonin et al. (2023) applies single isolates and synthetic communities (SynCom) on radish seeds to answer two key questions: what is the role of seed microbiota during the early stages of plant development? How can SynCom influence the seedling health and its microbiota? The study describes an elegant approach to cope with the variability of natural microbiota using SynCom following a gradient of complexity. Overall, the study highlighted a contrasted impact of the bacterial strains when applied in isolation or SynCom. The composition and complexity of the SynCom had also an impact on plant seedlings. Importantly, contrasting evolution from seeds to seedlings was observed for 3 strains of Pseudomonas fluorescens within the SynComs, underlining the importance of intra-species level diversity and precluding any generalization of results at species level. References Moreira, Z. P. M., Chen, M. Y., Ortuno, D. L. Y., & Haney, C. H. (2023). Engineering plant microbiomes by integrating eco-evolutionary principles into current strategies. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 71, 102316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102316 Simonin, M., Préveaux, A., Marais, C., Garin, T., Arnault, G., Sarniguet, A., & Barret, M. (2023). Transmission of synthetic seed bacterial communities to radish seedlings: impact on microbiota assembly and plant phenotype. bioRxiv, 2023-02. ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.14.527860 | Transmission of synthetic seed bacterial communities to radish seedlings: impact on microbiota assembly and plant phenotype | Marie Simonin, Anne Preveaux, Coralie Marais, Tiffany Garin, Gontran Arnault, Alain Sarniguet, Matthieu Barret | <p style="text-align: justify;">Seed-borne microorganisms can be pioneer taxa during germination and seedling emergence. Still, the identity and phenotypic effects of these taxa that constitute a primary inoculum of plant microbiota is mostly unkn... |  | Microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions, Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology, Microbiomes | Sebastien Massart | 2023-02-15 10:27:26 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Roey Angel
Anne Daebeler
Craig W. Herbold
Cédric Hubas
Melina Kerou
Katharina Kitzinger
David K. Ngugi










