Turnover statistics
Average time to find at least 2 reviewers after submission = 26 days (median = 17)
Average time from submission to 1st decision = 68 days (median = 57)
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers▲ | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
02 Mar 2023
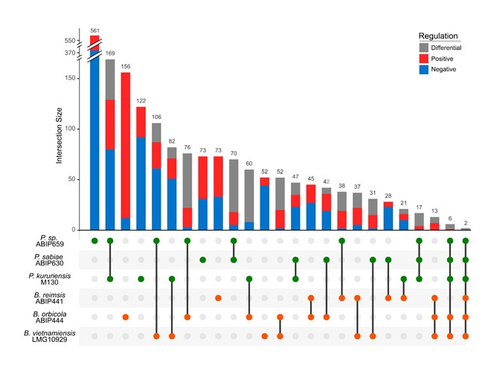
Comparative genomics and transcriptomic response to root exudates of six rice root-associated Burkholderia sensu lato speciesAdrian Wallner, Agnieszka Klonowska, Ludivine Guigard, Isabelle Rimbault, Eddy LM Ngonkeu, Phuong V Nguyen, Gilles Bena, Lionel Moulin https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.04.510755Burkholderia strains go it aloneRecommended by Romain Barnard based on reviews by Vittorio Venturi and 1 anonymous reviewerThe Burkholderia sensu lato group is predominant in the rhizosphere of rice. It includes both plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (typically members of the Paraburkholderia genus) and phytopathogens (typically members of the Burkholderia genus). Better understanding the interaction between Burkholderia sensu lato and their host plant is therefore crucial to advance our knowledge of the ecology of rice, a plant that feeds more than half of the humans on the planet. The perception of root exudates from their host is key for rhizobacteria. Is the response to root exudates more related to the phylogeny of the bacteria, i.e. genus-dependent, or is it strain-specific? This question is not trivial for the Burkholderia sensu lato group, which has experienced shifting outlines over the last twenty years. During the early stages of rice root colonization, Wallner et al. [1] investigated the transcriptomic regulation of three strains of each Burkholderia and Paraburkholderia genera, in addition to a genomic comparison, in order to better understand their early colonization strategies. While these six strains possess a large proportion of gene homologues, their experiment shows their response to root exudates to be strain-specific. In the study, rice root exudates affected several metabolic pathways of interest in most strains, noticeably including i) the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, which had never been reported to be activated in relation to root colonization and ii) the putrescine pathway, which may reflect signaling controlling root colonization. The work by Wallner et al. provides new insights on the strain-level response of the transcriptomic regulation of Burkholderia sensu lato in response to root exudates in the early stages of root colonization. Beyond this, the next steps will hopefully shed light on what happens in more complex environments, within a complex bacterial community and during later colonization stages.
Reference Wallner A, Klonowska A, Guigard L, King E, Rimbault I, Ngonkeu E, Nguyen P, Béna G, Moulin L (2022) Comparative genomics and transcriptomic response to root exudates of six rice root-associated Burkholderia sensu lato species. BioRxiv, 2022.10.04.510755, version 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.04.510755 | Comparative genomics and transcriptomic response to root exudates of six rice root-associated Burkholderia sensu lato species | Adrian Wallner, Agnieszka Klonowska, Ludivine Guigard, Isabelle Rimbault, Eddy LM Ngonkeu, Phuong V Nguyen, Gilles Bena, Lionel Moulin | <p>Beyond being a reliable nutrient provider, some bacteria will perceive the plant as a potential host and undertake root colonization leading to mutualistic or parasitic interactions. Bacteria of the <em>Burkholderia</em> and <em>Paraburkholderi... |  | Microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions, Microbial symbiosis | Romain Barnard | Kateryna Zhalnina , Trent Northern , Oscar Kuipers , Cara Haney , Joëlle Schläpfer , Vittorio Venturi, Anonymous, Steffen Kolb, Paulina Estrada-de los Santos | 2022-10-06 09:48:59 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Roey Angel
Anne Daebeler
Craig W. Herbold
Cédric Hubas
Melina Kerou
Katharina Kitzinger
David K. Ngugi










