Turnover statistics
Average time to find at least 2 reviewers after submission = 26 days (median = 17)
Average time from submission to 1st decision = 68 days (median = 57)
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▼ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
11 Aug 2023
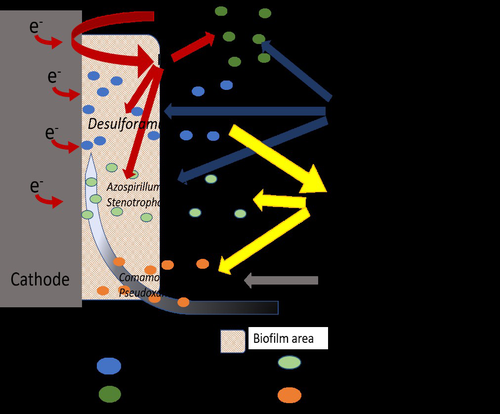
Comparison of enrichment methods for efficient nitrogen fixation on a biocathodeAxel Rous, Gaëlle Santa-Catalina, Elie Desmond-Le Quéméner, Eric Trably, Nicolas Bernet https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.02.530809Toward a low-energy bioelectrochemical fixation of N2 via mixed cultures electroactive biofilmsRecommended by Jo De Vrieze based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Nitrogen fixation and elimination are two key microbial processes that significantly impact the release (and removal) of reactive nitrogen into natural ecosystems. Unlike global change, caused by the emission of greenhouse gasses into our atmosphere, the release of reactive nitrogen into our biosphere only recently (in the last years) received the necessary public attention. Hence, novel techniques for (1) reactive nitrogen recovery, (2) energy-effective removal, and (3) sustainable nitrogen fixation are essential to prevent the nitrogen cycle from spinning out of control without also putting an additional burden on our precious natural resources or increasing the emission of greenhouse gasses. In this research paper by Rous et al. (2023), the authors investigated the use of a biocathode in a bioelectrochemical system (BES) for sustainable fixation of N2 into NH3, using electricity as a sustainable energy source and CO2 as the only carbon source. A critical element in their study was the enrichment of N2-fixating bacteria, starting from soil samples, in an effort to achieve effective nitrogen fixation. A comparison between the enriched culture and a pure culture of diazotrophic hydrogenotrophic bacteria confirmed comparable results for N2 fixation, indicating that the enrichment process was a viable and successful approach. Although pure culture biotechnological processes have their merits, it is clear that the usage of an enriched microbial culture allows for a more simple, robust, and open microbial process, compared to pure culture systems. This approach does enable a sustainable way of N2 (and by extension CO2) fixation, as it relies on electricity directly (or indirectly through H2) and CO2 only, but it does suffer from low coulombic efficiencies (<5%). This indicates that, even though the results are promising, there is room for optimization, especially concerning the production of (unwanted) side products, such as acetate and other microbial metabolites. This reflects a key challenge and potential disadvantage of mixed or enriched cultures compared to pure cultures. It is in that framework that this study provides an interesting, highly relevant view on the potential of bioelectrochemical nitrogen fixation using enriched cultures, yet, it also implies the need to either find a purpose for the byproducts, such as acetate, and/or achieve a more effective enrichment strategy to achieve an increased coulombic efficiency towards sustainable nitrogen fixation. | Comparison of enrichment methods for efficient nitrogen fixation on a biocathode | Axel Rous, Gaëlle Santa-Catalina, Elie Desmond-Le Quéméner, Eric Trably, Nicolas Bernet | <p>The production of nitrogen fertilizers in modern agriculture is mostly based on the Haber-Bosch process, representing nearly 2% of the total energy consumed in the world. Low-energy bioelectrochemical fixation of N2 to microbial biomass was pre... |  | Biofilms, microbial mats, Microbial biotechnology, Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology | Jo De Vrieze | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2023-03-07 08:27:42 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Roey Angel
Anne Daebeler
Craig W. Herbold
Cédric Hubas
Melina Kerou
Katharina Kitzinger
David K. Ngugi










