Turnover statistics
Average time to find at least 2 reviewers after submission = 26 days (median = 17)
Average time from submission to 1st decision = 68 days (median = 57)
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * ▲ | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
12 Apr 2024
Bacterial pathogens dynamic during multi-species infectionsMarie-Anne Barny, Sylvia Thieffry, Christelle Gomes de Faria, Elisa Thebault, Jacques Pedron https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.06.570389Unraveling disease ecology: insights from soft rot Pectobacteriaceae co-infectionsRecommended by Clara Torres-Barceló based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersFew studies deal with the understanding of disease ecology, especially in the agricultural domain. Soft rot Pectobacteriaceae are major plant pathogens that frequently co-infect potato tubers. Exploring their ecological relationships can provide valuable insights for effective monitoring and preventing disease. The study of Barny et al (2024) explores the dynamics of synthetic communities of soft rot Pectobacterium species (SRP) following in vitro and in vivo inoculations, focusing on the implications for disease development. To delve into co-infection dynamics, the authors constructed mixed populations comprising six strains, with three strains from each of two species. Through inoculations of both liquid cultures and potatoes, they observed outcomes using amplicon sequencing targeting the gapA gene, along with monitoring bacterial population sizes and symptoms on potato tubers. Results reveal intriguing patterns: competition among strains of the same species, cooperation through trophic interactions, and interference due to toxicity. Thanks to a modelling approach, they suggest that the presence of a cheater strain may be favoured when it is associated with an aggressive strain. This finding is crucial for field sampling strategies, as there is a risk that during an outbreak, only the cheater strain may be detected, potentially overlooking the problematic aggressive strain. While the study conducted by Barny et al. (2024) provides valuable insights into strain interactions, it also highlights areas for further exploration to enhance understanding. First, the extent to which different species occupy similar niches in real agricultural scenarios remains unclear. Additionally, comparative genomics analysis on strains and investigating specific gene candidates could offer valuable mechanistic insights into strain dynamics. These areas for future research offer chances to build up our knowledge base in this field and improve how we understand the interactions between bacteria in nature. The implications of the study extend beyond plant pathogens like SRP. Similar scenarios of complex diseases involving closely related species or strains competing within the same niche are observed in human pathogens as well. Reference Barny, M.-A., Thieffry, S., Gomes de Faria, C., Thebault, E., Pedron, J. (2024). Bacterial pathogens dynamic during multi-species infections. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.06.570389
| Bacterial pathogens dynamic during multi-species infections | Marie-Anne Barny, Sylvia Thieffry, Christelle Gomes de Faria, Elisa Thebault, Jacques Pedron | <p>Soft rot Pectobacteriacea (SRP) gathers more than 30 bacterial species that collectively rot a wide range of plants by producing and secreting a large set of plant cell wall degrading enzymes (PCWDEs). Worldwide potato field surveys identified ... | Microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions, Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology | Clara Torres-Barceló | 2023-12-12 17:54:07 | View | ||
29 Aug 2023
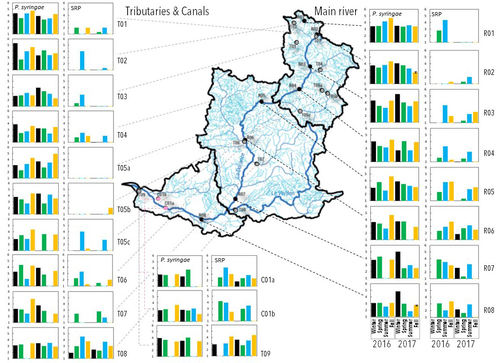
Comparative abundance and diversity of populations of the Pseudomonas syringae and Soft Rot Pectobacteriaceae species complexes throughout the Durance River catchment from its French Alps sources to its deltaC.E. Morris, C. Lacroix, C. Chandeysson, C. Guilbaud, C. Monteil, S. Piry, E. Rochelle Newall, S. Fiorini, F. Van Gijsegem, M.A. Barny, O. Berge https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.06.506731Treating all pathogens alike: a call for whole-catchment monitoring of plant-pathogensRecommended by Mina Bizic based on reviews by António Machado, Tiffany Lowe-Power and 1 anonymous reviewerPlant pathogens can cause devastating damage to crop (Strange and Scott 2005) greatly affecting a food resource in growing need on our planet. A significant proportion of global crops require irrigation, and with this, bare the risk of being affected by irrigation-borne pathogens (Lamichhane and Bartoli, 2015). Detection of plant pathogens in irrigation water can effectively be used to minimize this risk. River water makes up a major irrigation water source. Morris et al., (2023), propose monitoring whole river catchments to understand plant pathogen population dynamics and generate models to prevent outbreaks, similar to practices regarding water-borne human pathogens. Monitoring 270 km of the river Durance, Morris et al., (2023) reveal that two groups of bacteria known to host pathogenic strains, Pseudomonas syringae and the Soft Rot Pectobacteriaceae are present in relatively high numbers across the entire catchment or significant parts of it, respectively, with their abundance mostly correlated to water temperature. Nevertheless, despite their presence no major outbreaks have been reported in recent years. The authors suggest that the current environmental conditions in the lower, agriculture-dominated part of the catchment may not generate the necessary environment for an outbreak. Alternatively, as also suggested, though some potentially pathogenic variants were detected in the study, they may not match the crops currently grown in the area (Morris et al., 2023). The authors thus bring up the need for large scale monitoring and call for observations on potential land-use changes in the area that may alter the sensitive and seemingly stable conditions in such a way that outbreaks will be triggered. Change of land use, specifically from rural to agricultural use, has been repeatedly recognized to influence biodiversity (e.g., Ionescu et al., 2022). Furthermore, agricultural environments, with a dense network of irrigation channels, natural and man-made ponds, and larger reservoirs, will accelerate the spread of organisms through multiple biotic and abiotic vectors (Karnatak and Wollrab, 2020), and with this likely plant- (and other) pathogens. Overall, the work by Morris et al., (2023) highlights that studying the presence and distribution of plant pathogens in water used for irrigation across large areas, is bound to identify which potential pathogens are omnipresent, awaiting for the right condition for an outbreak; and which are rather spread from, isolated, local sources and thus can be effectively mitigated. References Strange, R. N., and Scott, P. R. (2005). Plant disease: a threat to global food security. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 43, 83–116. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.113004.133839 Lamichhane, J.R. and Bartoli, C. (2015), Plant pathogenic bacteria in open irrigation systems: what risk for crop health? Plant Pathol, 64: 757-766. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12371 C.E. Morris, C. Lacroix, C. Chandeysson, C. Guilbaud, C. Monteil, S. Piry, Rochelle Newall E., S. Fiorini, F. Van Gijsegem, M.A. Barny, O. Berge (2023) Comparative abundance and diversity of populations of the Pseudomonas syringae and Soft Rot Pectobacteriaceae species complexes throughout the Durance River catchment from its French Alps sources to its delta. bioRxiv, 2022.09.06.506731, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.09.06.506731 Ionescu, D., Bizic, M., Karnatak, R., Musseau, C. L., Onandia, G., Kasada, M., Berger, S. A., et al. (2022). From Microbes to Mammals: Pond Biodiversity Homogenization across Different Land-Use Types in an Agricultural Landscape. Ecological Monographs 92(3): e1523. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1523 | Comparative abundance and diversity of populations of the *Pseudomonas syringae* and Soft Rot *Pectobacteriaceae* species complexes throughout the Durance River catchment from its French Alps sources to its delta | C.E. Morris, C. Lacroix, C. Chandeysson, C. Guilbaud, C. Monteil, S. Piry, E. Rochelle Newall, S. Fiorini, F. Van Gijsegem, M.A. Barny, O. Berge | <p style="text-align: justify;">Rivers, creeks, streams are integrators of biological, chemical and physical processes occurring in a catchment linking land cover from the headwaters to the outlet. The dynamics of human and animal pathogens in cat... |  | Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology | Mina Bizic | 2022-12-22 12:04:32 | View | |
02 Mar 2023
Comparative genomics and transcriptomic response to root exudates of six rice root-associated Burkholderia sensu lato speciesAdrian Wallner, Agnieszka Klonowska, Ludivine Guigard, Isabelle Rimbault, Eddy LM Ngonkeu, Phuong V Nguyen, Gilles Bena, Lionel Moulin https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.04.510755Burkholderia strains go it aloneRecommended by Romain Barnard based on reviews by Vittorio Venturi and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Vittorio Venturi and 1 anonymous reviewer
The Burkholderia sensu lato group is predominant in the rhizosphere of rice. It includes both plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (typically members of the Paraburkholderia genus) and phytopathogens (typically members of the Burkholderia genus). Better understanding the interaction between Burkholderia sensu lato and their host plant is therefore crucial to advance our knowledge of the ecology of rice, a plant that feeds more than half of the humans on the planet. The perception of root exudates from their host is key for rhizobacteria. Is the response to root exudates more related to the phylogeny of the bacteria, i.e. genus-dependent, or is it strain-specific? This question is not trivial for the Burkholderia sensu lato group, which has experienced shifting outlines over the last twenty years. During the early stages of rice root colonization, Wallner et al. [1] investigated the transcriptomic regulation of three strains of each Burkholderia and Paraburkholderia genera, in addition to a genomic comparison, in order to better understand their early colonization strategies. While these six strains possess a large proportion of gene homologues, their experiment shows their response to root exudates to be strain-specific. In the study, rice root exudates affected several metabolic pathways of interest in most strains, noticeably including i) the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, which had never been reported to be activated in relation to root colonization and ii) the putrescine pathway, which may reflect signaling controlling root colonization. The work by Wallner et al. provides new insights on the strain-level response of the transcriptomic regulation of Burkholderia sensu lato in response to root exudates in the early stages of root colonization. Beyond this, the next steps will hopefully shed light on what happens in more complex environments, within a complex bacterial community and during later colonization stages.
Reference Wallner A, Klonowska A, Guigard L, King E, Rimbault I, Ngonkeu E, Nguyen P, Béna G, Moulin L (2022) Comparative genomics and transcriptomic response to root exudates of six rice root-associated Burkholderia sensu lato species. BioRxiv, 2022.10.04.510755, version 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.04.510755 | Comparative genomics and transcriptomic response to root exudates of six rice root-associated Burkholderia sensu lato species | Adrian Wallner, Agnieszka Klonowska, Ludivine Guigard, Isabelle Rimbault, Eddy LM Ngonkeu, Phuong V Nguyen, Gilles Bena, Lionel Moulin | <p>Beyond being a reliable nutrient provider, some bacteria will perceive the plant as a potential host and undertake root colonization leading to mutualistic or parasitic interactions. Bacteria of the <em>Burkholderia</em> and <em>Paraburkholderi... |  | Microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions, Microbial symbiosis | Romain Barnard | Kateryna Zhalnina , Trent Northern , Oscar Kuipers , Cara Haney , Joëlle Schläpfer , Vittorio Venturi, Anonymous, Steffen Kolb, Paulina Estrada-de los Santos | 2022-10-06 09:48:59 | View |
11 Aug 2023
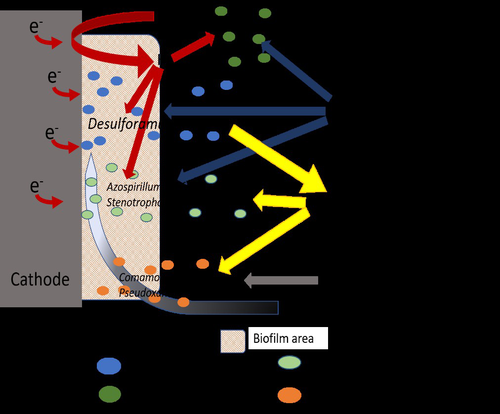
Comparison of enrichment methods for efficient nitrogen fixation on a biocathodeAxel Rous, Gaëlle Santa-Catalina, Elie Desmond-Le Quéméner, Eric Trably, Nicolas Bernet https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.02.530809Toward a low-energy bioelectrochemical fixation of N2 via mixed cultures electroactive biofilmsRecommended by Jo De Vrieze based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Nitrogen fixation and elimination are two key microbial processes that significantly impact the release (and removal) of reactive nitrogen into natural ecosystems. Unlike global change, caused by the emission of greenhouse gasses into our atmosphere, the release of reactive nitrogen into our biosphere only recently (in the last years) received the necessary public attention. Hence, novel techniques for (1) reactive nitrogen recovery, (2) energy-effective removal, and (3) sustainable nitrogen fixation are essential to prevent the nitrogen cycle from spinning out of control without also putting an additional burden on our precious natural resources or increasing the emission of greenhouse gasses. In this research paper by Rous et al. (2023), the authors investigated the use of a biocathode in a bioelectrochemical system (BES) for sustainable fixation of N2 into NH3, using electricity as a sustainable energy source and CO2 as the only carbon source. A critical element in their study was the enrichment of N2-fixating bacteria, starting from soil samples, in an effort to achieve effective nitrogen fixation. A comparison between the enriched culture and a pure culture of diazotrophic hydrogenotrophic bacteria confirmed comparable results for N2 fixation, indicating that the enrichment process was a viable and successful approach. Although pure culture biotechnological processes have their merits, it is clear that the usage of an enriched microbial culture allows for a more simple, robust, and open microbial process, compared to pure culture systems. This approach does enable a sustainable way of N2 (and by extension CO2) fixation, as it relies on electricity directly (or indirectly through H2) and CO2 only, but it does suffer from low coulombic efficiencies (<5%). This indicates that, even though the results are promising, there is room for optimization, especially concerning the production of (unwanted) side products, such as acetate and other microbial metabolites. This reflects a key challenge and potential disadvantage of mixed or enriched cultures compared to pure cultures. It is in that framework that this study provides an interesting, highly relevant view on the potential of bioelectrochemical nitrogen fixation using enriched cultures, yet, it also implies the need to either find a purpose for the byproducts, such as acetate, and/or achieve a more effective enrichment strategy to achieve an increased coulombic efficiency towards sustainable nitrogen fixation. | Comparison of enrichment methods for efficient nitrogen fixation on a biocathode | Axel Rous, Gaëlle Santa-Catalina, Elie Desmond-Le Quéméner, Eric Trably, Nicolas Bernet | <p>The production of nitrogen fertilizers in modern agriculture is mostly based on the Haber-Bosch process, representing nearly 2% of the total energy consumed in the world. Low-energy bioelectrochemical fixation of N2 to microbial biomass was pre... |  | Biofilms, microbial mats, Microbial biotechnology, Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology | Jo De Vrieze | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2023-03-07 08:27:42 | View |
29 Aug 2023
Comparison of metabarcoding taxonomic markers to describe fungal communities in fermented foodsOlivier Rué, Monika Coton, Eric Dugat-Bony, Kate Howell, Françoise Irlinger, Jean-Luc Legras, Valentin Loux, Elisa Michel, Jérôme Mounier, Cécile Neuvéglise, Delphine Sicard https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.13.523754Towards a more accurate metabarcoding approach for studying fungal communities of fermented foodsRecommended by Caroline Strub based on reviews by Johannes Schweichhart and 2 anonymous reviewersImproved characterization of food microbial ecosystems, especially those fermented is key to the development of food sustainability. Short-read metabarcoding is one of the most popular ways to study microbial communities. However, this approach remains complex because of the locks and biases it may entail particularly when applied to fungal communities. Building and using four mock communities from fermented food (bread, wine, cheese, fermented meat), Rué et al., 2023 demonstrate that combined DADA2 denoising algorithm followed to the FROGS tools gives a more accurate description of fungal communities compared to several commonly used bioinformatic workflows, dealing with all amplicon lengths. Moreover, Rué et al., 2023 provide guidance on which barcode to use (ITS1, ITS2, D1/D2 and RPB2), depending on the fermented food studied. Practices in metabarcoding of fungi have been recently reviewed by Tedersoo et al., 2022 and their synthesis comes to the same conclusion as Rué et al., 2023. As the reference databases are far from being complete notably for food ecosystems, the development of specific sequences public databases will enable the scientific community to lift the veil on this whole area of microbial ecology. The study conducted by Rué et al. (2023) provides a particularly detailed approach from a technical point of view, which contributes to improving the general practices in the metabarcoding of fungi. The design and the use of mock communities to compare the performances of the different pipelines is a strong point of this study. Another key element is the creation and use of an in-house database of fungal barcode sequences which improved the species-level affiliations However, the study of fungal communities by metabarcoding is still a promising avenue of research in agri-food sciences. Thus, short-read sequencing, combined with suitable pipelines and databases, should remain of interest to the microbial ecology community (Pauvert et al., 2019; Furneaux et al., 2021). References Furneaux, B., Bahram, M., Rosling, A., Yorou, N. S., & Ryberg, M. (2021). Long‐and short‐read metabarcoding technologies reveal similar spatiotemporal structures in fungal communities. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21(6), 1833-1849. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.13387 Pauvert, C., Buée, M., Laval, V., Edel-Hermann, V., Fauchery, L., Gautier, A., ... & Vacher, C. (2019). Bioinformatics matters: The accuracy of plant and soil fungal community data is highly dependent on the metabarcoding pipeline. Fungal Ecology, 41, 23-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2019.03.005 Rué, O., Coton, M., Dugat-Bony, E., Howell, K., Irlinger, F., Legras, J. L., ... & Sicard, D. (2023). Comparison of metabarcoding taxonomic markers to describe fungal communities in fermented foods. BioRxiv, 2023-0113.523754, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.13.523754 Tedersoo, L., Bahram, M., Zinger, L., Nilsson, R. H., Kennedy, P. G., Yang, T., ... & Mikryukov, V. (2022). Best practices in metabarcoding of fungi: From experimental design to results. Molecular ecology, 31(10), 2769-2795. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.16460 | Comparison of metabarcoding taxonomic markers to describe fungal communities in fermented foods | Olivier Rué, Monika Coton, Eric Dugat-Bony, Kate Howell, Françoise Irlinger, Jean-Luc Legras, Valentin Loux, Elisa Michel, Jérôme Mounier, Cécile Neuvéglise, Delphine Sicard | <p>Next generation sequencing offers several ways to study microbial communities. For agri-food sciences, identifying species in diverse food ecosystems is key for both food sustainability and food security. The aim of this study was to compare me... |  | Bioinformatics dedicated to microbial studies | Caroline Strub | 2023-01-20 12:37:03 | View | |
04 Jan 2024
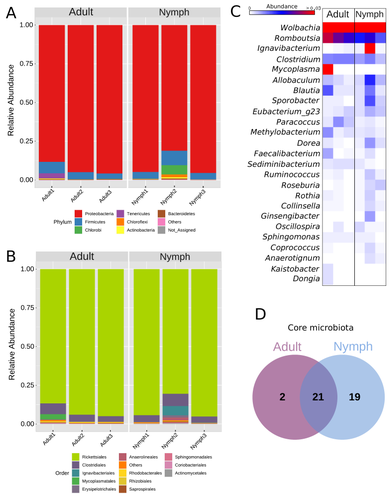
Diversity of bacterial symbionts associated with the tropical plant bug Monalonion velezangeli (Hemiptera: Miridae) revealed by high-throughput 16S-rRNA sequencingLucio Navarro-Escalante, Pablo Benavides, Flor Edith Acevedo https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2022560/v7Shedding light on bacteria associated with an agricultural pest, the tropical plant bug Monalonion velezangeli: a foundational descriptive studyRecommended by Jean-Marie Volland based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The paper "Diversity of bacterial symbionts associated with the tropical plant bug Monalonion velezangeli (Hemiptera: Miridae) revealed by high-throughput 16S rRNA sequencing" by Navarro-Escalante et al. (2023) is a valuable contribution to entomological research, particularly in the context of pest management. This descriptive study, while not delving into the functional characterization of the associated bacterial strains, lays an essential groundwork for understanding the bacterial components of the microbiota of this agricultural pest. This study is interesting because it provides new information on insect microbiota, especially in a family for which the knowledge of the diversity of bacterial symbionts is very limited. One of the study's core strengths lies in its exploration and definition of the core microbiota of M. velezangeli, which could serve as a foundation for future research aimed at pest control strategies. The use of 16S rRNA sequencing, despite its known limitations, has enabled the profiling of these bacterial communities. The paper highlights the absence of differences in the bacterial communities associated with the nymph and adult stages of the pest, indicating a stable association of these microbes throughout the insect's life cycle. A standout point in the study is the overwhelming presence of the symbiont Wolbachia, accounting for approximately 92% of the bacterial composition. However, intriguingly, the authors also note the absence of Wolbachia in some individuals, suggesting a more complex dynamic that warrants further investigation. This finding is particularly noteworthy, as it opens up questions about the role of Wolbachia and its impact on the biology and ecology of M. velezangeli. The researchers have carefully addressed all the reviewers’ comments and suggestions. They also addressed a potential bias in their study - the overwhelming presence of Wolbachia - by analyzing the bacterial community after the removal of Wolbachia sequences. This careful approach enriches the study's credibility and ensures a more accurate representation of the pest's microbiota. The identification of potentially culturable strains within the core microbiome represents an interesting perspective of this research. This information could be used in future efforts to develop pest control strategies, particularly those employing paratransgenic approaches. The possibility of manipulating these culturable strains to combat M. velezangeli presents an exciting avenue for sustainable pest management. While the study does not investigate the localization of these associated bacteria, whether in the gut or elsewhere, including potentially in dedicated symbiotic organs, it nevertheless offers a valuable descriptive account. This baseline knowledge will be useful for any subsequent functional or localization studies, which could further unravel the complex interactions between M. velezangeli and its microbial partners. In conclusion, the work of Navarro-Escalante et al. is a notable effort to set the stage for future research into the biology of M. velezangeli and its associated microbiota. The findings from this study provide a good reference point for further investigations aimed at pest's biology and exploring innovative pest control strategies. It also represents a valuable contribution to understanding the basic biology of insect-bacteria interactions.
| Diversity of bacterial symbionts associated with the tropical plant bug *Monalonion velezangeli* (Hemiptera: Miridae) revealed by high-throughput 16S-rRNA sequencing | Lucio Navarro-Escalante, Pablo Benavides, Flor Edith Acevedo | <p>Insects and microbes have developed complex symbiotic relationships that evolutionarily and ecologically play beneficial roles for both, the symbiont and the host. In most Hemiptera insects, bacterial symbionts offer mainly nutritional, defensi... |  | Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology, Microbial symbiosis | Jean-Marie Volland | 2022-10-31 20:31:54 | View | |
13 Oct 2023
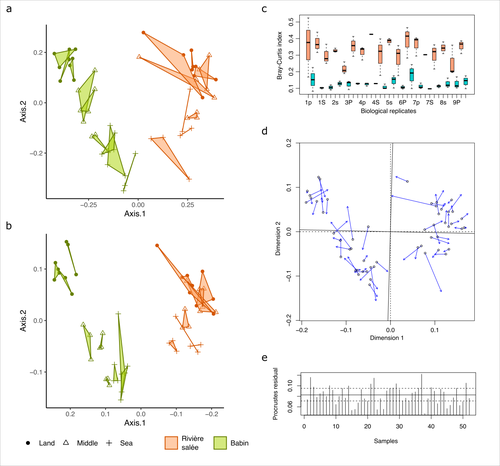
Fine-scale congruence in bacterial community structure from marine sediments sequenced by short-reads on Illumina and long-reads on NanoporeAlice Lemoinne, Guillaume Dirberg, Myriam Georges, Tony Robinet https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.06.541006ONT long-read sequencing and Illumina short-read sequencing of 16S rDNA amplicons give comparable results in terms of bacterial community structure in marine sedimentsRecommended by Aymé Spor based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
ONT long-read high-throughput sequencing is not routinely used for metabarcoding studies of microbial communities. Even though this technology is supposed to considerably improve phylogenetic coverage and taxonomic resolution, it initially suffered from relatively poor read accuracy. Assessment of the performance of this new approach in comparison with routinely used 16S rDNA short-read sequencing is therefore needed to validate its use. The study by Lemoinne et al. (2023) offers a comprehensive comparison of two 16S rDNA metabarcoding approaches on marine sediment samples. By comparing Illumina short-read sequencing with ONT long-read sequencing, the authors conclude that bacterial community structures inferred from both technologies were similar. They also found that differences observed between sampling sites and along the sea-land orientation were comparable between the two technologies. However, the choice of technology still has an impact on the obtained results, notably in terms of bacterial diversity retrieved, taxonomic resolution, and replicability between biological replicates. Altogether, these results validate the use of ONT long-read sequencing for 16S metabarcoding approaches in marine sediments. Comparisons of such kinds targeting other remote environments are needed, as they might offer new opportunities for field scientists with no access to sequencing platforms to study the structure and composition of microbial communities. Reference Lemoinne, A., Dirberg, G., Georges, M., & Robinet, T. (2023). Fine-scale congruence in bacterial community structure from marine sediments sequenced by short-reads on Illumina and long-reads on Nanopore. biorXiv, version 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.06.541006 | Fine-scale congruence in bacterial community structure from marine sediments sequenced by short-reads on Illumina and long-reads on Nanopore | Alice Lemoinne, Guillaume Dirberg, Myriam Georges, Tony Robinet | <p style="text-align: justify;">Following the development of high-throughput sequencers, environmental prokaryotic communities are usually described by metabarcoding with genetic markers on the 16S domain. However, short-read sequencing encounters... |  | Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology, Molecular microbiology | Aymé Spor | 2023-06-07 17:48:08 | View | |
25 Apr 2023
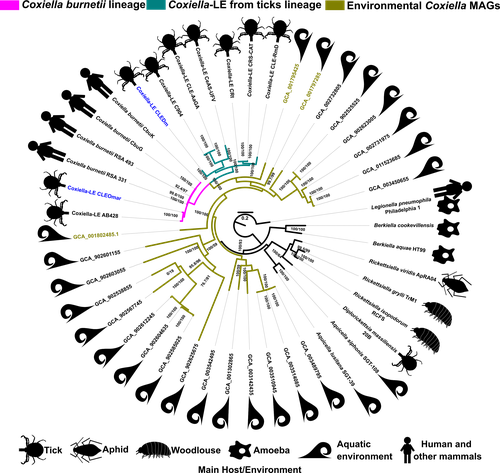
Genomic Changes During the Evolution of the Coxiella Genus Along the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum.Diego Santos-Garcia, Olivier Morel, Hélène Henri, Adil El Filali, Marie Buysse, Valérie Noël, Karen D. McCoy, Yuval Gottlieb, Lisa Klasson, Lionel Zenner, Olivier Duron, Fabrice Vavre https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.26.513839Lifestyle transitions in endosymbiosisRecommended by Daniel Tamarit based on reviews by Sophie Abby, Adam Ossowicki and 1 anonymous reviewerHost-microbe symbioses are an essential component of many ecological systems, playing critical roles in the physiology and evolution of all involved partners. In this context, the bacterial family that includes Coxiella burnetii, the causative agent of Q fever, is of particular interest. The Coxiellaceae family is a complex group with members that have adopted a variety of specializations. Closely related lineages to C. burnetii are tick mutualists (Coxiella-like endosymbionts) and aquatic bacteria that may include both free living and symbiotic species. Additionally, four related genera within this family include symbionts of insects and amoebae. Exactly how and when pathogenicity and mutualism evolved in this lineage is not clear, thus remaining a valuable line of enquiry that can help establish general principles on these lifestyle transitions. A new study by Santos-Garcia and colleagues (2023) places the spotlight on this bacterial group, obtaining new insights through comparative genomics. The authors add two genomes, one of them a circular contig representing a highly reduced (0.9 Mb) chromosome, that increase the resolution of key branches in the Coxiella evolutionary tree. These include a sister group to C. burnetii and the group immediately subtending them, both entirely containing Coxiella-like endosymbionts. By analyzing genetic potential for metabolism, cell dimorphism, virulence and acidophily, the authors find evidence for the ancestrality of genes associated with a pathogenic lifestyle, and support a scenario by which mutualism arose multiple times in a parasitic lineage. In this context shines a pathogenicity island acquired in the common ancestor of this group and subsequently eroded in mutualistic lineages. This scenario highlights the importance of pre-adaptations that facilitate evolutionary specializations, such as the capabilities for B vitamin biosynthesis (key feature in the adaptation to a mutualistic relationship with organisms with B-vitamin-poor diets) and pH homeostasis (harnessed by C. burnetii for infection). Microbial groups at the crossroads of parasitism and mutualism help us understand the mechanisms underpinning these evolutionary strategies (see e.g. Drew et al, 2021). Transitions in endosymbiosis, including shifts in the parasitism-mutualism continuum, adaptation to new partners, or switches between free-living and host-associated lifestyles, affect the structure of ecological networks, and understanding them can yield crucial insights into how to manipulate microbial symbioses for health outcomes, sustainable agriculture or ecosystem conservation. The Coxiellaceae, by including a diverse set of mutualistic, parasitic and possibly free-living lineages, are a fantastic model group to tackle these questions. Together with other host-associated bacteria, such as Sodalis (Clayton et al, 2012) or Pantoea (Walterson and Stavrinides, 2015) species, these ecologically diverse microbes are valuable assets in the quest to decipher the molecular basis of lifestyle transitions in endosymbiosis. REFERENCES Clayton, A.L., et al (2012). A novel human-infection-derived bacterium provides insights into the evolutionary origins of mutualistic insect–bacterial symbioses. PLoS Genetics, 8: e1002990. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002990 Drew, G.C., Stevens, E.J., King, K.C. (2021). Microbial evolution and transitions along the parasite-mutualist continuum. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 19: 623-638. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00550-7 Santos-Garcia, D., et al. (2023) Genomic changes during the evolution of the Coxiella genus along the parasitism-mutualism continuum. bioRxiv, 2022.10.26.513839, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.26.513839 Walterson, A.M., Stavrinides, J. (2015). Pantoea: insights into a highly versatile and diverse genus within the Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 39: 968-984. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuv027 | Genomic Changes During the Evolution of the Coxiella Genus Along the Parasitism-Mutualism Continuum. | Diego Santos-Garcia, Olivier Morel, Hélène Henri, Adil El Filali, Marie Buysse, Valérie Noël, Karen D. McCoy, Yuval Gottlieb, Lisa Klasson, Lionel Zenner, Olivier Duron, Fabrice Vavre | <p style="text-align: justify;">The Coxiellaceae family is composed of five genera showing lifestyles ranging from free-living to symbiosis. Among them, <em>Coxiella burnetii </em>is a well-known pathogen causing Q fever in humans. This bacterium ... |  | Bioinformatics dedicated to microbial studies, Genomic and evolutionary studies, Microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions, Microbial symbiosis | Daniel Tamarit | 2022-10-27 12:55:14 | View | |
09 May 2023
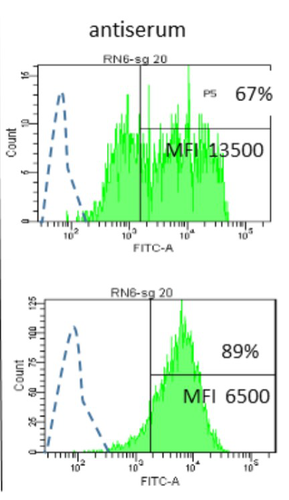
Interactions between Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides and bovine macrophages under physiological conditionsPhilippe Totté, Tiffany Bonnefois, Lucia Manso-Silvan https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.06.519279Interaction of bovine macrophages with Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoidesRecommended by Pablo Zunino based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersMycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides (Mmm), a pathogenic wall-less bacterium, is the etiological agent of contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (CBPP). This highly contagious respiratory disease may develop in severe pneumonia, with associated high mortality rates in cattle. Mmm can display different immune evasion mechanisms; in addition, a host uncontrolled inflammatory response stands for lung lesions and chronic carrier animals. Macrophages are among the most important lines of defense against Mmm of the lower respiratory tract. Although their importance in defense and immune response modulation is known, results about their role and mechanisms of action are scarce and sometimes conflicting. In the present study, Totté et al. (1) aimed to investigate the interaction of bovine macrophages (isolated from cattle peripheral blood mononuclear cells) with Mmm, under in vitro conditions. The authors highlight that the study was performed under physiological conditions (in the presence of complement prepared from the same cell donor). In their study, using different approaches, the authors provide interesting and original results, proposing a pivotal role of complement in controlling the inflammatory response, which is crucial in the CBPP pathogenesis. The authors reported that macrophages did not kill Mmm in the presence of a non-bactericidal concentration of bovine serum. However, Mmm inactivation was observed when antiserum from CBPP convalescent animals was used. They also observed that Mmm induced the production of TNF by macrophages (when a high MOI was assessed). However, complement could even abolish Mmm-induced TNF response when used at bactericidal activity concentrations. This role of complement could be combined with the development of potentially protective antibodies against particular Mmm antigens involved in the interaction with identified macrophage receptors to propose control strategies against CBPP. Overall, the study by Totté et al. provides new fundamental insight for the research on preventive or therapeutic strategies for a poorly understood disease that still represents a serious concern for livestock production. REFERENCES 1. Totté, P., Bonnefois, T., Manso-Silván, L. Interactions between Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides and bovine macrophages under physiological conditions. bioRxiv 2022.12.06.519279, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Microbiology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.06.519279 | Interactions between *Mycoplasma mycoides* subsp. *mycoides* and bovine macrophages under physiological conditions | Philippe Totté, Tiffany Bonnefois, Lucia Manso-Silvan | <p style="text-align: justify;">Abstract</p> <p>We investigated the interactions of unopsonized and opsonized *Mycoplasma mycoides* subsp. *mycoides* (Mmm) with bovine macrophages *in vitro*. Mmm survived and proliferated extracellularly on bovin... |  | Microbe-microbe and microbe-host interactions | Pablo Zunino | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-12-09 15:12:53 | View |
19 Jul 2024
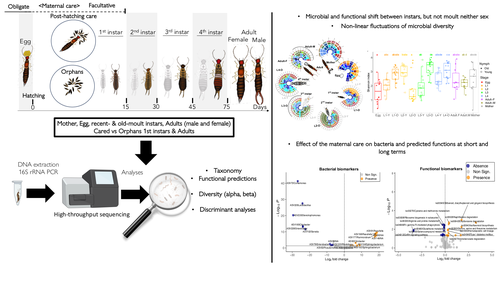
Microbiome turnover during offspring development varies with maternal care, but not moult, in a hemimetabolous insectMarie-Charlotte Cheutin, Manon Boucicot, Joel Meunier https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.26.586808Stability in a microbe-insect interactionRecommended by Konstantinos (Kostas) Kormas based on reviews by Guillame Minard and Enric Frago based on reviews by Guillame Minard and Enric Frago
The degree of fidelity between microbes and their hosts varies considerably among different animal groups but also along the host's developmental stages and depends on the stability of their microbial communities. Cheutin et al. showcase experimentally the stability of whole body bacterial microbiome in a dermapteran insect species, the European earwig Forficula auricularia. The carefully designed experiments, which include a large number of investigated families and the related methodologies along with the data analysis, revealed that the bacterial communities of this insect are highly dynamic during the early developmental stages, but these changes are rather specific to each developmental stage and rather irrelevant to moulting. Some of these changes were reflected in the dominant predicted metabolic pathways. Another important finding of this study was that maternal care of the eggs has a detectable impact on the future shaping of the adult insect bacterial microbiome. The findings of this paper clearly answer its working hypotheses, but they also generate a set of specific novel hypotheses for future studies. These hypotheses are of interest to the general field of animal-microbe interactions and, more specifically, to the driving forces of transmissability of microbes from one generation to the next one. This study also depicts some of the most likely important metabolic pathways in this insect-microbe relationship that could be the focus of future studies with more specific methodologies. References Cheutin M-C, Boucicot M, Meunier J. (2024). Microbiome turnover during offspring development varies with maternal care, but not moult, in a hemimetabolous insect. bioRxiv, ver.3, peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Microbiology. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.03.26.586808v3 | Microbiome turnover during offspring development varies with maternal care, but not moult, in a hemimetabolous insect | Marie-Charlotte Cheutin, Manon Boucicot, Joel Meunier | <p>The ecological success of insects often depends on their association with beneficial microbes. However, insect development involves repeated moults, which can have dramatic effects on their microbial communities. Here, we investigated whether a... |  | Microbial ecology and environmental microbiology, Microbial physiology, ecophysiology and metabolism, Microbiomes | Konstantinos (Kostas) Kormas | 2024-03-28 12:24:50 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Roey Angel
Anne Daebeler
Craig W. Herbold
Cédric Hubas
Melina Kerou
Katharina Kitzinger
David K. Ngugi










